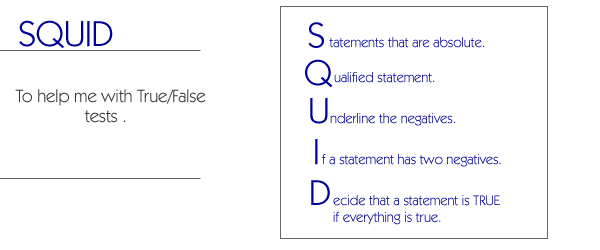
S tatements
that are absolute are usually false.
- Words such as these represent absolutes:
all, every, never, and no are usually FALSE.
- Examples: All animals are reptiles;
Every person in the Congress is a man.
|
|
Q
ualified statements are usually true.
- Words such as these represent qualifiers:
some, most, and sometimes are usually TRUE.
- Examples: Some animals are reptiles.
Most of the people in the Congress are men.
|
 |
U nderline
the negatives.
- Words such as these are negatives:
not, cannot, do not, no, the prefix in(incomplete)
and the prefix un(unimportant) in each statement.
- Examples: Washington D.C. is not
the capital of the United States. 365 days is an incomplete
year.
|
|
I f
a statement has 2 negatives, cross out both negatives.
- Cross out both of the negatives and
read the sentence without them. This will clearly show the
meaning.
- Examples: People will
not
buy luxury goods if they do not have disposable
income. People will buy luxury goods if they have disposable
income.
|
 |
D ecide
that a statement is TRUE only if EVERYTHING about the statement
is true.
- Items on a test often include information
that is true except for a detail, so pay close attention to
the complete statement.
- Examples: Massachusetts, Virginia,
and Pennsylvania were all part of the original 13 colonies
(true because all 3 were part of the original 13 colonies).
Massachusetts, Virginia, and Montana were all part of the
original 13 colonies (not true because Montana was not one
of the original 13 colonies).
|
|
|