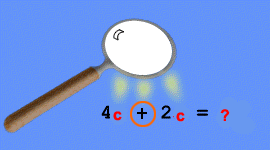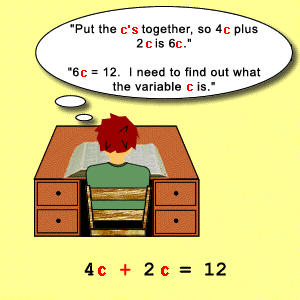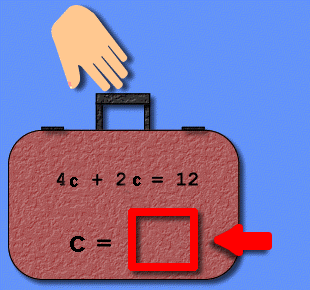F
ind what you are solving for.
-
Look for the question
mark.
-
Underline the information
that tells you what you are solving for.
-
Name the variable
(what you are solving for) with a letter and write it after
the question mark.
|
|
A
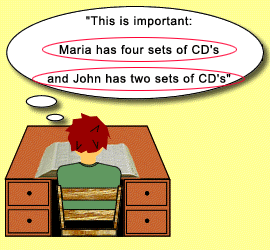
sk yourself, "What is
the important information?"
-
- Find the number phrases and circle them.
|
|
-
Write the equation with
the variables and the numbers in the correct order.
|
|
Take the
equation and solve it.
-
Solve the equation and
write the answer.
-
If you can't solve
the equation, then use "DRAW" to solve it.
|
|
D
iscover the variable and the operations.
- Scan the equation and look for operation
signs (+, -, x, ÷).
- Circle the operation sign.
|
|
R
ead the equation and
combine like terms.
-
Read the whole
equation out loud.
-
- For example, numbers
that have the same letter next to them: 6a + 2a + 5 + 2
= 15. Both "6a" and "2a" are like terms.
Also, numbers without letters next to them are like terms
("5" & "2").
- Combine like terms.
- For example, "6a" and
"2a" can be combined (6a + 2a = "8a").
Also, "5" and "2" can be combined (5
+ 2 = "7").
6a + 2a + 5 + 2 = 15 now becomes 8a + 7 = 15.
|
|
A nswer
the equation, or draw and check.
-
See example
of how to draw the solution.
|
|
| Write
the answer for the variable and check the equation.
- Write the number that represents the answer.
- Substitute your answer for the letter in the original equation.
- For example:
6a + 2a + 5 + 2 = 15
6(1) + 2(1) + 5 + 2 = 15
- Work the problem and see if the left side equals the right
side.
- For example:
6(1) + 2(1) + 5 + 2 = 15
(6 x 1) + (2 x 1) + 5 + 2 = 15
6 + 2 + 5 + 2 = 15
15 = 15
|
|